Sophisticated Phishing Attacks: Targeting Victims Through Trusted Websites and Real-Time Verification

The threat research team has identified a sophisticated phishing incident that employs legitimate infrastructure, precise email validation, and evasive delivery techniques. This case exemplifies the exploitation of trusted domains, server-side phishing email validation, and highlights the pressing requirement for robust, browser-based zero-day phishing defense mechanisms.
Incident Overview
In a real-world setting, the browser security solution was configured to operate in silent mode, allowing comprehensive monitoring of user interactions and threat indicators without disrupting the user experience. This approach granted the security team visibility into the various stages of the phishing attempt, facilitating a thorough evaluation of attack vectors, user behaviors, and detection accuracy.
Credential Theft Detection
Upon reviewing managed detections, the research team detected authentication-related phishing cues while in silent mode, signaling that an employee had submitted credentials on a dubious webpage. This configuration allowed the complete observation of the attempted credential theft, revealing intricate attacker methodologies.
Utilizing insights obtained via the browser security extension, the team rapidly assessed the chained phishing attack, confirmed credential input, and initiated remediation actions—including resetting the user’s password and scrutinizing any atypical account or login behavior.

Employing default safeguards from the security solution effectively halted such interactions. Moreover, telemetry data indicated no browser activity occurring prior to accessing the phishing pages, suggesting the user likely interacted with an email application—common in scenarios where phishing starts in email but transitions to a browser environment.
In this incident, the employee clicked on a link pointing to a legitimate website that hosted an illicit page.
Campaign Overview
1) Hosting on a Legitimate Domain
The targeted individual accessed a reputable domain—established for nine years and recognized for selling tents—which had been compromised to deliver a malicious form page located at /memo/home.html. Upon visiting this link, the user encountered a prompt claiming that a “Confidential Document” was available, urging them to provide their email to download a payment PDF. Such social engineering techniques are frequently employed to elicit user credentials by presenting a false need for access.
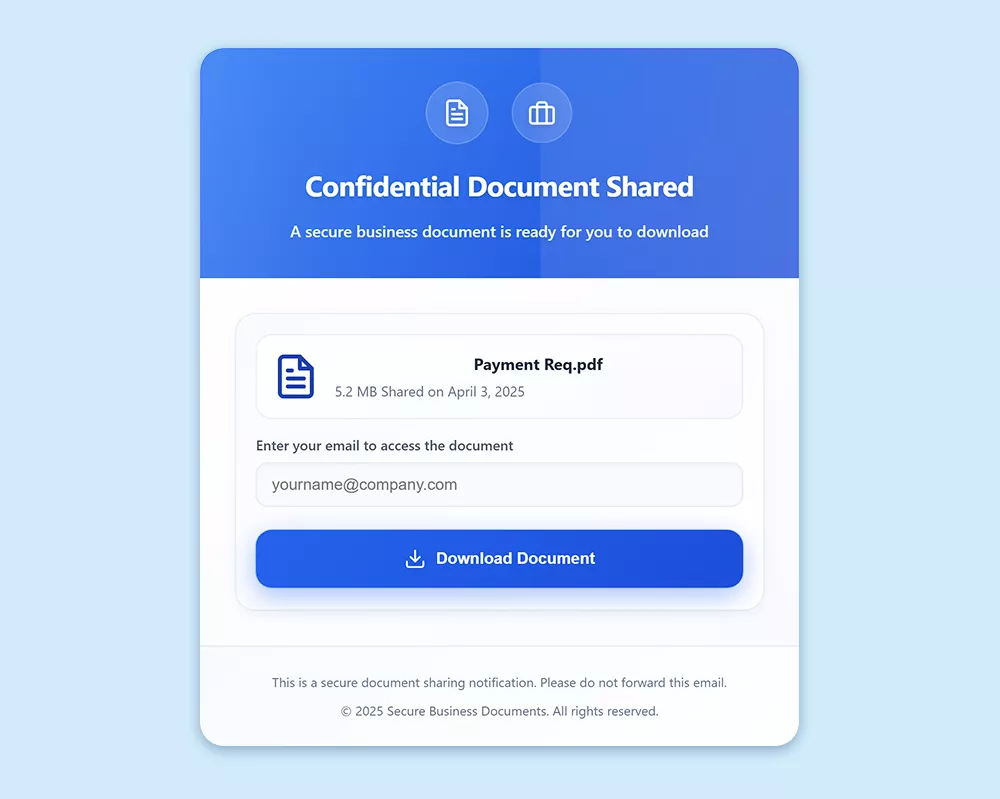
Basic Evasion Techniques
This malicious page integrated fundamental anti-analysis features, such as disabling right-click context menus and blocking common keyboard shortcuts to deter users from inspecting or saving content. These basic protections are commonly employed to obstruct analysis efforts.

Dynamic Email Handling
The phishing infrastructure featured logic to manage email input dynamically, adjusting based on how the victim arrived at the page. If the phishing link contained the victim’s email within the URL’s anchor, the JavaScript would automatically populate the form, minimizing friction and raising the likelihood of credential submission.
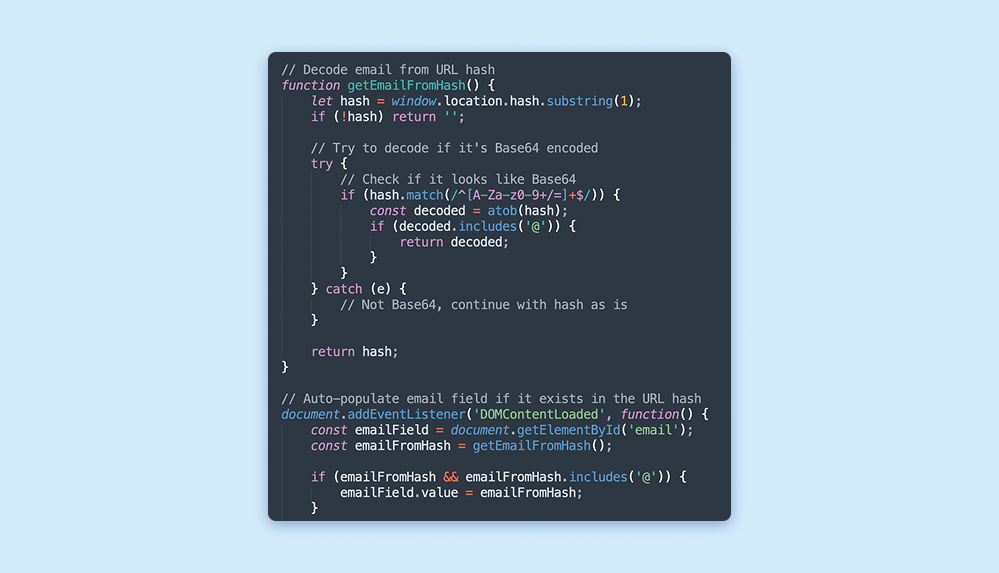
Email Submission Process
If no email is detected in the anchor, the form requires the victim to manually enter their email. Upon submission, the user is redirected to another malicious site while simultaneously transmitting their email to an API endpoint. This advanced framework allows for real-time email validation, tailoring further interactions with the user based on the input provided.
2) CAPTCHA Implementation
Post-email submission, users faced a Cloudflare CAPTCHA challenge before advancing to the final phishing page. This strategy serves multiple purposes, including thwarting automated analysis and enhancing the legitimacy of the phishing operation.
.png)
3) Customized Phishing Page
Post-CAPTCHA, the phishing page may present a fake Microsoft login form, with the displayed page contingent on the email submitted. Specified behaviors include:
- Personal email (e.g., @gmail.com): The page leads to a blank screen.
- Corporate email (valid but not on the attacker’s list): The page showcases a generic Microsoft login form.
- Targeted email (valid and on the attack list): The page displays a customized login form branded with the victim’s company logo and information.

This indicates the backend performs server-side email validation, adjusting the phishing payload based on whether the email aligns with specific targets.
Precision-Validated Phishing
This advanced technique ensures that only the designated targets receive the final phishing page, accomplished via server-side email validation. The attacker’s infrastructure utilizes backend APIs to streamline the phishing process and enhance evasion against standard detection mechanisms.
Counteracting Precision Phishing
Despite its complexities, the primary goal remains straightforward: credential theft. Ensuring your security apparatus can thwart phishing attempts before user interaction is critical. Strategies include:
- Implementing measures to identify and block phishing pages across all domains, including trusted ones.
- Investing in solutions that recognize impersonations of primary business platforms.
- Providing employees with real-time protection at the browser level, extending beyond mere email filtering.
Staying Ahead of Evolving Threats
As phishing tactics continue to evolve, leveraging genuine infrastructure and validation techniques, the solution remains evident: proactive, in-browser protection is vital. Preventing user engagement with fraudulent login pages is the most effective approach to halting phishing activities at their inception.
To explore how our solutions can fortify defenses against phishing threats, request a personalized demonstration with our team.








