“Emergence of the ‘Russian Market’ as a Principal Source for Compromised Credentials”

The “Russian Market” cybercrime marketplace has gained significant traction as a prominent platform for trading credentials compromised by information stealer malware. Active for approximately six years, the marketplace saw an upsurge in popularity around 2022, with recent reports indicating further increases in user engagement. This growth can be partially attributed to the takedown of the Genesis Market, which created a substantial gap in the marketplace landscape.
A considerable portion of the credentials (85%) sold through the Russian Market are recycled from existing sources. Nonetheless, the market has gained a substantial cybercriminal following due to its extensive inventory and the availability of logs at prices starting as low as $2.
An infostealer log typically comprises a text file or a collection of files generated by infostealer malware, containing account passwords, session cookies, credit card information, cryptocurrency wallet data, and system profiling details extracted from compromised devices.
Each log can encompass tens to thousands of credentials, potentially aggregating hundreds of millions of stolen credentials. Following their collection, these logs are uploaded to an attacker’s server for further exploitation or resale on platforms like the Russian Market.
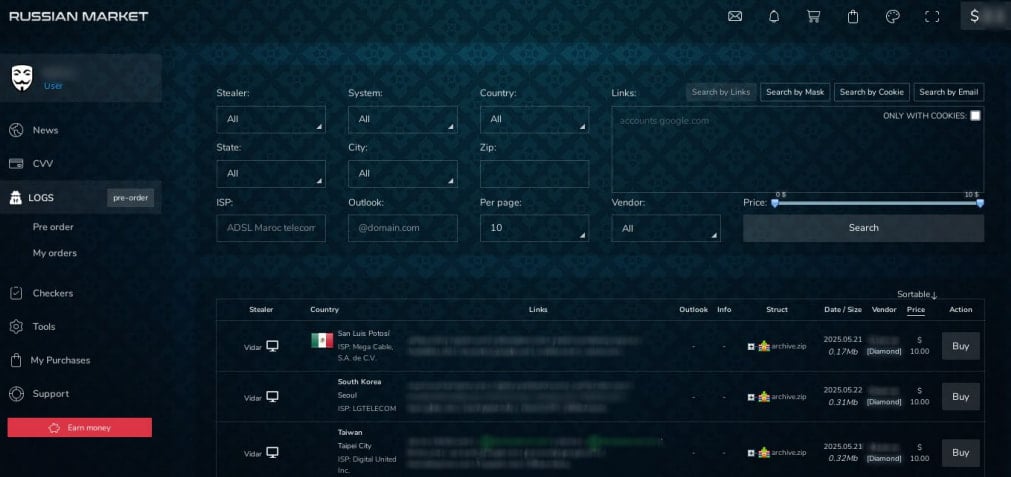
The use of infostealers has surged among threat actors, with multiple campaigns now targeting enterprises to pilfer session cookies and corporate credentials.
According to findings, 61% of the logs obtained from the Russian Market consist of Software as a Service (SaaS) credentials from platforms such as Google Workspace, Zoom, and Salesforce, while 77% incorporate Single Sign-On (SSO) credentials.
Researchers highlight that compromised cloud accounts grant adversaries access to critical systems, thereby creating prime conditions for sensitive data theft.
Trends in Infostealer Usage
Recent analysis of over 1.6 million listings on the Russian Market reveals significant fluctuations in the popularity of specific infostealer variants.
Historically, the Lumma stealer dominated the market, accounting for 92% of all credential logs available for sale. Its prominence peaked following the downfall of Raccoon Stealer, which faced significant law enforcement setbacks. However, a similar situation now looms over Lumma, as its activities have recently been disrupted by a coordinated global law enforcement campaign, resulting in the seizure of 2,300 associated domains.
The long-term impact of this disruption is still being assessed, with reports indicating that Lumma’s developers are actively seeking to reestablish their operations.
Simultaneously, a new infostealer named Acreed is rapidly gaining momentum, having uploaded over 4,000 logs during its initial week of operations subsequent to Lumma’s disruption.
Acreed targets a range of information typical of this type of malware, including data from browsers like Chrome and Firefox, encompassing passwords, cookies, cryptocurrency wallets, and credit card information.
Infostealer infections primarily occur through phishing campaigns, ClickFix attacks, and malvertising related to premium software, as well as social media platforms like YouTube and TikTok. Maintaining vigilance and adhering to best practices for software downloads are essential to mitigating this pervasive threat.








