Phishing Attempt Concealed in Deceptive DocuSign Email
On a routine security assessment, a phishing attempt was identified that employed a clever delivery mechanism. What appeared to be a standard DocuSign notification evolved into a sophisticated deception involving Webflow, a misleading redirect, and a legitimate Google login interface.
Webflow is a visual website creation tool that enables designers and developers to build custom, responsive websites without requiring code. Users can visually develop, construct, and deploy websites directly in the browser.
The incident commenced with an email impersonating a known contact and referencing a completed DocuSign document.

The email successfully passed SPF, DKIM, and DMARC checks, lending it an unfounded sense of authenticity. The link purportedly leading to “view the completed document” redirected to a Webflow preview URL. Such links are often employed by designers for prototyping websites. This raised suspicions but did not immediately indicate malicious intent.
However, preview links are not standard for legitimate DocuSign requests, which typically direct users to the following domains:
- docusign.com
- docusign.net
- docusign.eu (for European users)
By routing through a recognized Webflow domain, the perpetrators minimized the likelihood of the initial stage being blocked.
Despite the risks, interaction was executed in a controlled environment to investigate further. The Webflow preview masqueraded as a DocuSign interface, featuring a single button: “View Document.”
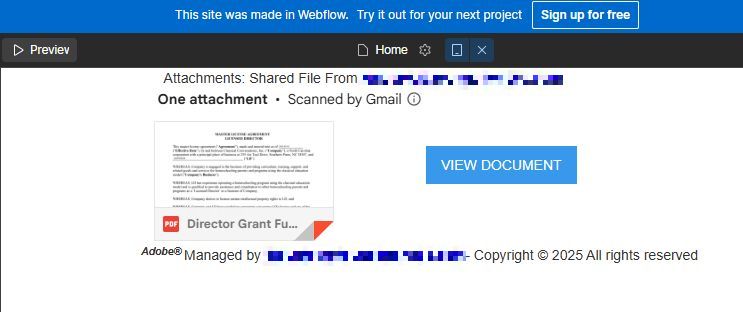
This link directed to a domain that raised immediate concerns:
sjw.ywmzoebuntt.es
The domain appeared as a random string, a common tactic employed in phishing to circumvent reputation-based security measures.
Clicking the “View document” button led to a deceptive Captcha, designed not to deter users.
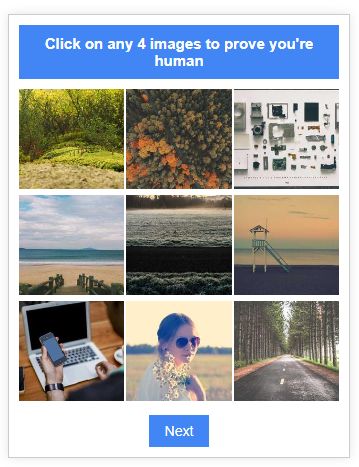
Captchas are often utilized in phishing schemes to create an illusion of legitimate security verification, yet this implementation set an uncharacteristically low threshold for validation. The prompt to “click on any 4 images to prove you’re human” represented a minimal challenge.
Once this step was navigated, the user was redirected to the authentic Google login page. This approach enables attackers to remain unnoticed and severely underappreciated as a form of cyber threat.
The sequence of events likely involved the malicious link initially displaying a cloaked page aimed at collecting user data. It may have gathered browser metadata, such as IP addresses, user agent details, language preferences, and screen resolution, then redirected the user to Google, enhancing the illusion of security. The system may have identified that the user was not the intended target based on fingerprinting, consequently directing them to an innocuous site.
This method exemplified a dual-purpose phishing strategy, incorporating reconnaissance to identify potential victims and refining subsequent attacks. The link triggered a range of suspicious activities, including probing system identifiers and altering user registry entries.
If an individual has interacted with a link of this nature, it is advisable to take the following precautions:
- Clear browser cache and cookies.
- Review account login history for unusual activity.
- Activate two-factor authentication if it is not already in place.
- Execute a comprehensive antivirus and malware scan.
It is essential to remember that a lack of visible malware does not imply that the phishing attempt was ineffective; it may indicate that the attackers are merely beginning their efforts.
This specific attack exhibited characteristics of highly targeted phishing. To mitigate the risk of falling victim, the following strategies should be employed:
- Avoid clicking on links in unsolicited emails. Verify the sender’s identity through a separate communication method before proceeding.
- Familiarize yourself with standard operating procedures to recognize atypical behaviors that may serve as red flags.
- Utilize an effective antimalware solution with web protection to enhance security.
Cybersecurity risks should not extend beyond reporting; proactive measures and effective solutions are vital in safeguarding digital assets.








