Russian Espionage Operation Aimed at Entities Connected to the Ukraine Conflict
A recent cyber espionage campaign attributed to Russian hackers is actively targeting organizations associated with the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. This operation, named “Operation RoundPress” by ESET, has been in progress since at least 2023 and is primarily executed by the group known as Fancy Bear. Its main aim is to extract sensitive data from specific email accounts within its targeted organizations.
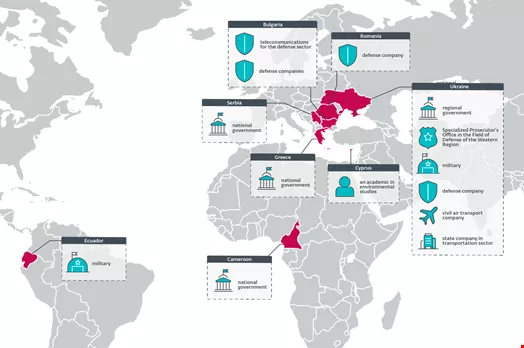
The operation focuses on Ukrainian governmental bodies and defense contractors located in Bulgaria and Romania, many of which produce Soviet-era military equipment intended for Ukraine. ESET has also identified attacks on governmental entities across Africa, Europe, and South America.
The attack mechanism centers around spearphishing emails that exploit cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities to inject malicious JavaScript into the target’s webmail interface. In 2024, ESET noted a variety of XSS vulnerabilities being exploited against multiple webmail platforms, including Roundcube, Horde, MDaemon, and Zimbra.
Research indicates that Fancy Bear typically disseminates these XSS vulnerabilities via email, allowing the malicious code to execute within the browser environment of the webmail client, potentially exposing sensitive information from the compromised accounts. Successful execution of this exploit hinges on the target opening the compromised email in a vulnerable webmail environment, rendering effective spam filtering and persuasive subject lines critical for the attackers. Examples of subject lines found in these spearphishing campaigns include, “SBU arrested a banker who worked for enemy military intelligence in Kharkiv,” and “Putin seeks Trump’s acceptance of Russian conditions in bilateral relations.”
Once a target engages with the email, the attackers deploy a series of JavaScript payloads—namely SpyPress.HORDE, SpyPress.MDAEMON, SpyPress.ROUNDCUBE, and SpyPress.ZIMBRA—designed to steal login credentials, exfiltrate email data, and sometimes compromise two-factor authentication (2FA), thereby granting persistent access to the victim’s mailbox.
Initially concentrating on Roundcube in 2023, Fancy Bear expanded its targeting to include additional webmail services in 2024. The MDaemon vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-11182, was a zero-day exploit likely discovered by the attackers. In contrast, those affecting Horde, Roundcube, and Zimbra were recognized vulnerabilities that had been previously patched.
Industry experts note that the continued targeting of webmail servers such as Roundcube and Zimbra by various espionage groups, including Fancy Bear, can be attributed to a lack of updates in many organizations’ webmail infrastructures. The vulnerabilities can be exploited remotely through emails, making such platforms attractive targets for information theft.
In their report, ESET provides a thorough analysis of the JavaScript payloads utilized in this campaign.
Fancy Bear, also referred to as Sednit, APT28, Pawn Storm, Forest Blizzard, and Sofacy Group, is a prominent Russian cyber espionage group linked to the military intelligence agency GRU since its inception in 2004. Following an indictment by the U.S. Special Counsel in 2018, Fancy Bear was identified as GRU Unit 26165. The group also gained notoriety for its involvement in key incidents, including the hacking of the Democratic National Committee (DNC) before the 2016 U.S. elections, as well as attacks against networks like TV5Monde and the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).